A neural network is a series of algorithms that endeavors to recognize underlying relationships in a set of data through a process that mimics the way the human brain operates. In this sense, neural networks refer to systems of neurons, either organic or artificial in nature.
Neural networks can adapt to changing input; so the network generates the best possible result without needing to redesign the output criteria. The concept of neural networks, which has its roots in artificial intelligence, is swiftly gaining popularity in the development of trading systems.
Linear Neural NetworkThe neural network without any activation function in any of its layers is called a linear neural network. The neural network which has action functions like relu, sigmoid or tanh in any of its layer or even in more than one layer is called non-linear neural network.

- Neural networks are a series of algorithms that mimic the operations of an animal brain to recognize relationships between vast amounts of data.
- As such, they tend to resemble the connections of neurons and synapses found in the brain.
- They are used in a variety of applications in financial services, from forecasting and marketing research to fraud detection and risk assessment.
- Neural networks with several process layers are known as "deep" networks and are used for deep learning algorithms
- The success of neural networks for stock market price prediction varies.
Hidden layers fine-tune the input weightings until the neural network’s margin of error is minimal. It is hypothesized that hidden layers extrapolate salient features in the input data that have predictive power regarding the outputs. This describes feature extraction, which accomplishes a utility similar to statistical techniques such as principal component analysis.
Linear regression may be both the simplest and most popular among the standard tools to regression. Dating back to the dawn of the 19th century, linear regression flows from a few simple assumptions. First, we assume that the relationship between the independent variables x and the dependent variable y is linear, i.e., that y can be expressed as a weighted sum of the elements in x, given some noise on the observations. Second, we assume that any noise is well-behaved
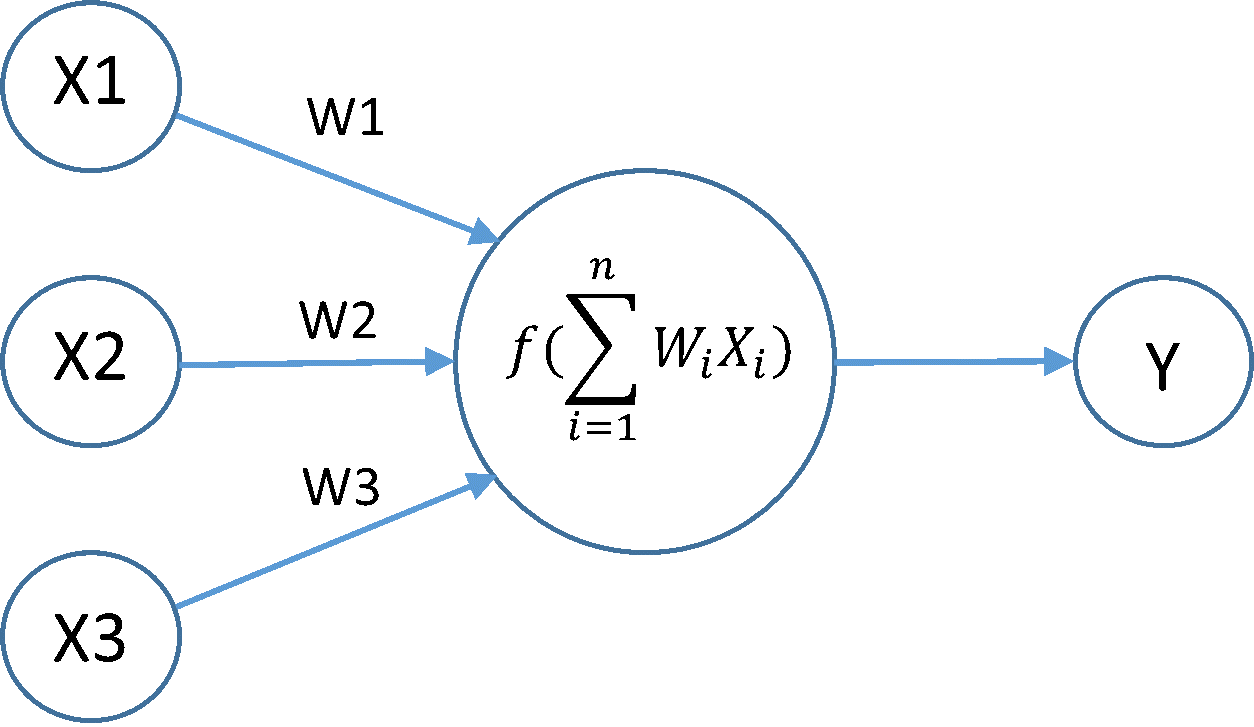
The loss function quantifies the distance between the real and predicted value of the target. The loss will usually be a non-negative number where smaller values are better and perfect predictions incur a loss of 0. The most popular loss function in regression problems is the squared error.

The sigmoid function is used as an activation function in neural networks. Just to review what is an activation function, the figure below shows the role of an activation function in one layer of a neural network. A weighted sum of inputs is passed through an activation function and this output serves as an input to the next layer.
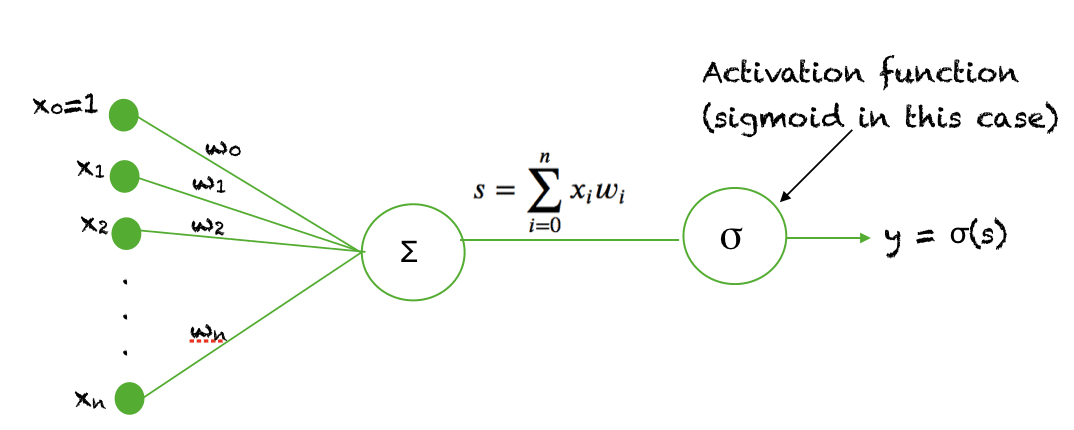
When the activation function for a neuron is a sigmoid function it is a guarantee that the output of this unit will always be between 0 and 1. Also, as the sigmoid is a non-linear function, the output of this unit would be a non-linear function of the weighted sum of inputs. Such a neuron that employs a sigmoid function as an activation function is termed as a sigmoid unit.
